27 Road Fuel Break
The 27 Road Fuel Break Project is designed to reduce wildfire risk by creating a fire break—up to 1,000 feet wide—along parts of the 27 Road. The road was identified as a key location for a fuel break because it runs primarily north-south and borders the Badger Creek Wilderness and adjacent state and private lands.
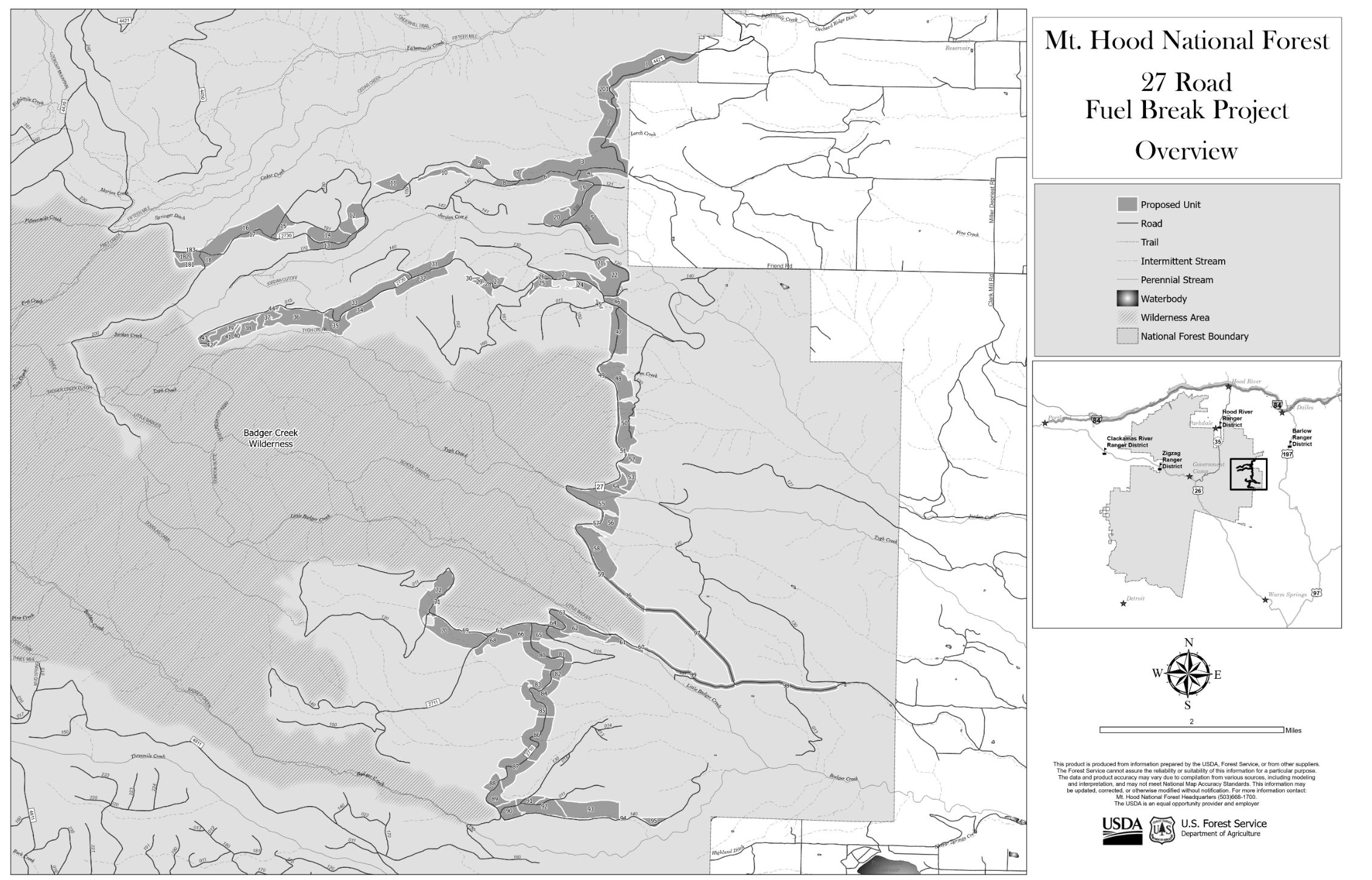
Map showing the location of the 27 Road Fuel Break treatment units.
Implementation of the fuel break involves thinning overly dense forest across about 2,800 acres to provide anchor points for firefighters and improve the safety of nearby communities. Crews will use a method called thinning from below, which means removing the smaller, more crowded trees while keeping the biggest, healthiest ones. This helps reduce ladder fuels and improve growing conditions for the remaining trees.
Different techniques will be used to implement the project depending on the area—some will use machines, others will use hand crews. Treatments may include cutting and removing trees, grinding brush (mastication), piling debris, and using controlled burns.
The goal is to reduce the number of trees and brush enough to slow wildfires, while still keeping a healthy forest. This includes keeping some young trees to support natural regeneration and a mix of tree ages.
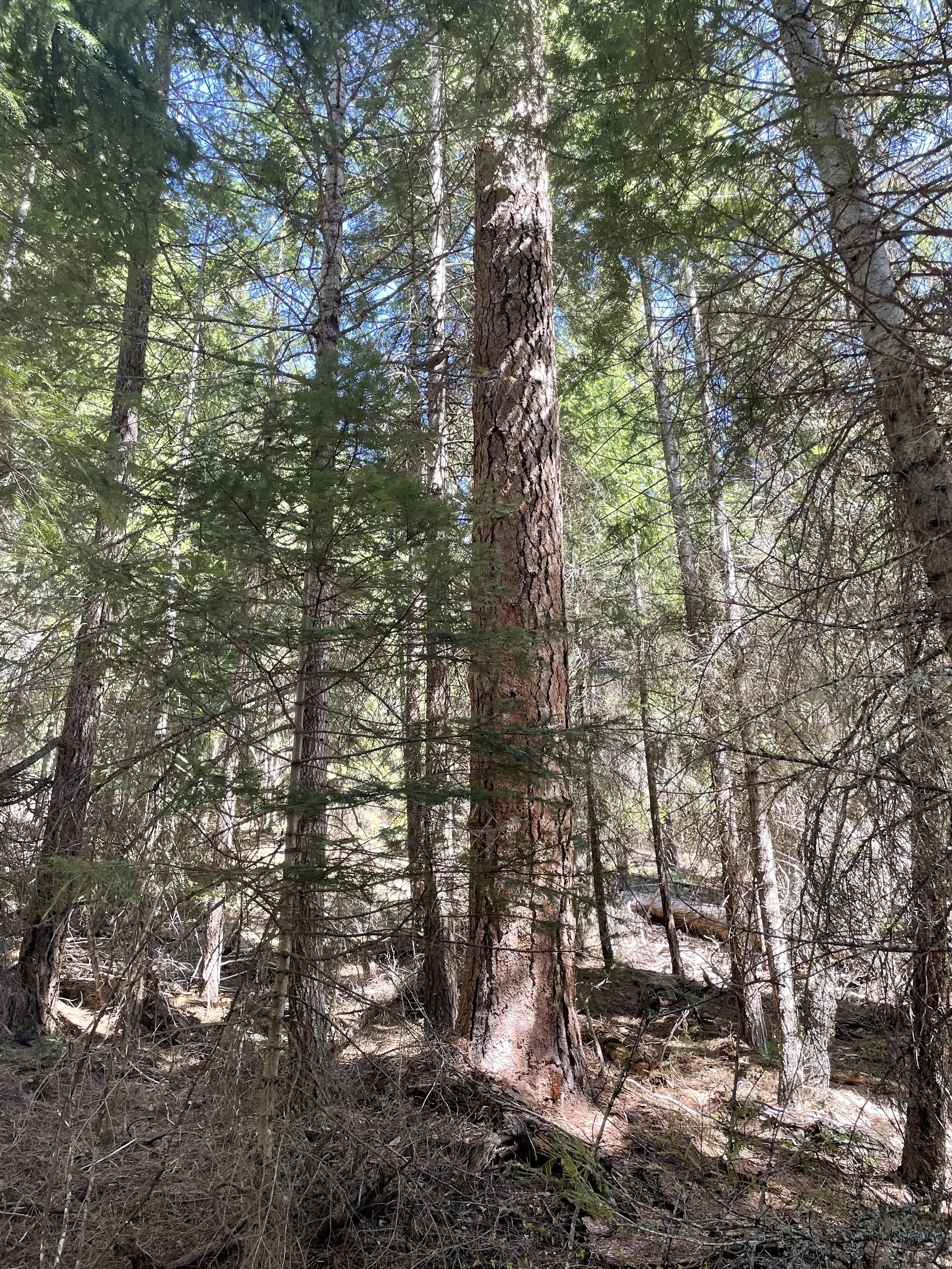
Image of a legacy Ponderosa Pine, a tree species that is especially fire and drought-tolerant, surrounded by young trees that have encroached due to the lack of fire and disturbance in the ecosystem. The 27 Road Fuel Break will remove these smaller trees and ladder fuels, improving both forest health and fire fighter safety.
To learn more about the project visit the Mt. Hood National Forest website here.